Python dictionary is a data structure that stores the value in key: value pairs. Values in a dictionary can be of any data type and can be duplicated, whereas keys can't be repeated and must be immutable.
Example: Here, The data is stored in key:value pairs in dictionaries, which makes it easier to find values.
Python
d = {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
print(d)
Output{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
How to Create a Dictionary
Dictionary can be created by placing a sequence of elements within curly {} braces, separated by a 'comma'.
Python
d1 = {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
print(d1)
# create dictionary using dict() constructor
d2 = dict(a = "Geeks", b = "for", c = "Geeks")
print(d2)
Output{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
{'a': 'Geeks', 'b': 'for', 'c': 'Geeks'}
- Dictionary keys are case sensitive: the same name but different cases of Key will be treated distinctly.
- Keys must be immutable: This means keys can be strings, numbers or tuples but not lists.
- Keys must be unique: Duplicate keys are not allowed and any duplicate key will overwrite the previous value.
- Dictionary internally uses Hashing. Hence, operations like search, insert, delete can be performed in Constant Time.
From Python 3.7 Version onward, Python dictionary are Ordered.
Accessing Dictionary Items
We can access a value from a dictionary by using the key within square brackets or get() method.
Python
d = { "name": "Prajjwal", 1: "Python", (1, 2): [1,2,4] }
# Access using key
print(d["name"])
# Access using get()
print(d.get("name"))
Adding and Updating Dictionary Items
We can add new key-value pairs or update existing keys by using assignment.
Python
d = {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
# Adding a new key-value pair
d["age"] = 22
# Updating an existing value
d[1] = "Python dict"
print(d)
Output{1: 'Python dict', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks', 'age': 22}
Removing Dictionary Items
We can remove items from dictionary using the following methods:
- del: Removes an item by key.
- pop(): Removes an item by key and returns its value.
- clear(): Empties the dictionary.
- popitem(): Removes and returns the last key-value pair.
Python
d = {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks', 'age':22}
# Using del to remove an item
del d["age"]
print(d)
# Using pop() to remove an item and return the value
val = d.pop(1)
print(val)
# Using popitem to removes and returns
# the last key-value pair.
key, val = d.popitem()
print(f"Key: {key}, Value: {val}")
# Clear all items from the dictionary
d.clear()
print(d)
Output{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
Geeks
Key: 3, Value: Geeks
{}
Iterating Through a Dictionary
We can iterate over keys [using keys() method] , values [using values() method] or both [using item() method] with a for loop.
Python
d = {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 'age':22}
# Iterate over keys
for key in d:
print(key)
# Iterate over values
for value in d.values():
print(value)
# Iterate over key-value pairs
for key, value in d.items():
print(f"{key}: {value}")
Output1
2
age
Geeks
For
22
1: Geeks
2: For
age: 22
Read in detail: Ways to Iterating Over a Dictionary
Nested Dictionaries
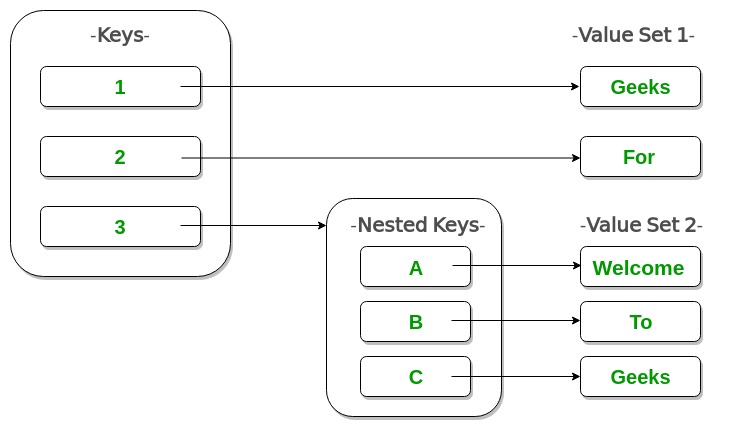
Example of Nested Dictionary:
Python
d = {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For',
3: {'A': 'Welcome', 'B': 'To', 'C': 'Geeks'}}
print(d)
Output{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: {'A': 'Welcome', 'B': 'To', 'C': 'Geeks'}}
Read in Detail: Python Nested Dictionary
Copying Dictionaries in Python
A copy of a dictionary can be created using either shallow copy or deep copy methods. These methods allow duplicating dictionary objects, but they behave differently when it comes to nested data. Let's dicuss both in detail.
1. Shallow Copy
A shallow copy makes a new dictionary with same outer values as the original. But if the dictionary has nested data (like a list or another dictionary), both copies still share that inner data. So, changes to nested parts will affect other.
It is created using copy.copy() method from Python’s copy module.
Example:
This code shows that in a shallow copy, changes to nested data affect both the original and the copy because the nested parts are shared.
Python
import copy
original = {'name': 'Alice', 'marks': {'math': 90, 'science': 95}}
# Create a shallow copy
shallow = copy.copy(original)
# Modify nested value in the copy
shallow['marks']['math'] = 100
print("Original:", original)
print("Shallow Copy:", shallow)
OutputOriginal: {'name': 'Alice', 'marks': {'math': 100, 'science': 95}}
Shallow Copy: {'name': 'Alice', 'marks': {'math': 100, 'science': 95}}
Explanation:
- shallow = copy.copy(original): creates a shallow copy, nested 'marks' remains shared.
- shallow['marks']['math'] = 100: updates 'math' in the shared nested dictionary.
- print(original), print(shallow): both show updated 'math' value due to shared data.
2. Deep Copy
A deep copy makes a new dictionary and also creates separate copies of all nested data (like lists or other dictionaries). This means original and copy are completely independent, changes made to nested parts do not affect other.
It is created using copy.deepcopy() method from Python’s copy module.
Example:
This Example shows that a deep copy creates a fully independent copy of both the outer and nested data, so changes in the copy do not affect the original.
Python
import copy
original = {'name': 'Alice', 'marks': {'math': 90, 'science': 95}}
# Create a deep copy
deep = copy.deepcopy(original)
# Modify nested value in the deep copy
deep['marks']['math'] = 100
print("Original:", original)
print("Deep Copy:", deep)
OutputOriginal: {'name': 'Alice', 'marks': {'math': 90, 'science': 95}}
Deep Copy: {'name': 'Alice', 'marks': {'math': 100, 'science': 95}}
Explanation:
- deep = copy.deepcopy(original): creates a deep copy, nested 'marks' is also copied separately.
- deep['marks']['math'] = 100: updates 'math' in the deep copy’s nested dictionary only.
- print(original), print(deep): original remains unchanged, only deep copy shows the updated 'math' value.
Python Dictionary Operation Programs
Python Dictionary Problems
Related Dictionary Articles
Similar Reads
Dictionaries in Python Python dictionary is a data structure that stores the value in key: value pairs. Values in a dictionary can be of any data type and can be duplicated, whereas keys can't be repeated and must be immutable. Example: Here, The data is stored in key:value pairs in dictionaries, which makes it easier to
7 min read
How to Create a Dictionary in Python The task of creating a dictionary in Python involves storing key-value pairs in a structured and efficient manner, enabling quick lookups and modifications. A dictionary is an unordered, mutable data structure where each key must be unique and immutable, while values can be of any data type. For exa
3 min read
Python - Add Dictionary Items In Python, dictionaries are a built-in data structure that stores key-value pairs. Adding items to a dictionary is a common operation when you're working with dynamic data or building complex data structures. This article covers various methods for adding items to a dictionary in Python.Adding Items
3 min read
Python Add Dictionary Key In Python, dictionaries are unordered collections of key-value pairs. Each item in a dictionary is accessed by its unique key, which allows for efficient storage and retrieval of data. While dictionaries are commonly used with existing keys, adding a new key is an essential operation when working wi
4 min read
Python Access Dictionary In Python, dictionaries are powerful and flexible data structures used to store collections of data in key-value pairs. To get or "access" a value stored in a dictionary, we need to know the corresponding key. In this article, we will explore all the ways to access dictionary values, keys, and both
4 min read
Python Change Dictionary Item A common task when working with dictionaries is updating or changing the values associated with specific keys. This article will explore various ways to change dictionary items in Python.1. Changing a Dictionary Value Using KeyIn Python, dictionaries allow us to modify the value of an existing key.
3 min read
Python Remove Dictionary Item Sometimes, we may need to remove a specific item from a dictionary to update its structure. For example, consider the dictionary d = {'x': 100, 'y': 200, 'z': 300}. If we want to remove the item associated with the key 'y', several methods can help achieve this. Let’s explore these methods.Using pop
2 min read
Get length of dictionary in Python Python provides multiple methods to get the length, and we can apply these methods to both simple and nested dictionaries. Let’s explore the various methods.Using Len() FunctionTo calculate the length of a dictionary, we can use Python built-in len() method. It method returns the number of keys in d
3 min read
Python - Value length dictionary Sometimes, while working with a Python dictionary, we can have problems in which we need to map the value of the dictionary to its length. This kind of application can come in many domains including web development and day-day programming. Let us discuss certain ways in which this task can be perfor
4 min read
Python - Dictionary values String Length Summation Sometimes, while working with Python dictionaries we can have problem in which we need to perform the summation of all the string lengths which as present as dictionary values. This can have application in many domains such as web development and day-day programming. Lets discuss certain ways in whi
4 min read