Read, Write and Parse JSON using Python
Last Updated :
12 Jul, 2025
JSON is a lightweight data format for data interchange that can be easily read and written by humans, and easily parsed and generated by machines. It is a complete language-independent text format. To work with JSON data, Python has a built-in package called JSON.
Example of JSON String
s = '{"id":01, "name": "Emily", "language": ["C++", "Python"]}'The syntax of JSON is considered a subset of the syntax of JavaScript including the following:
- Name/Value pairs: Represents Data, the name is followed by a colon(:), and the Name/Value pairs are separated by a comma(,).
- Curly braces: Holds objects.
- Square brackets: Hold arrays with values separated by a comma (,).
Keys/Name must be strings with double quotes and values must be data types amongst the following:
Example of JSON file:
{
"employee": [
{
"id": "01",
"name": "Amit",
"department": "Sales"
},
{
"id": "04",
"name": "sunil",
"department": "HR"
}
]
}Python Parse JSON String
In the below code, we are going to convert JSON to a Python object. To parse JSON string Python firstly we import the JSON module. We have a JSON string stored in a variable 'employee' and we convert this JSON string to a Python object using json.loads() method of JSON module in Python. After that, we print the name of an employee using the key 'name' .
Python3
# Python program to convert JSON to Python
import json
# JSON string
employee ='{"id":"09", "name": "Nitin", "department":"Finance"}'
# Convert string to Python dict
employee_dict = json.loads(employee)
print(employee_dict)
print(employee_dict['name'])
Output{'id': '09', 'name': 'Nitin', 'department': 'Finance'}
Nitin
Python read JSON file
Let's suppose we have a JSON file that looks like this.
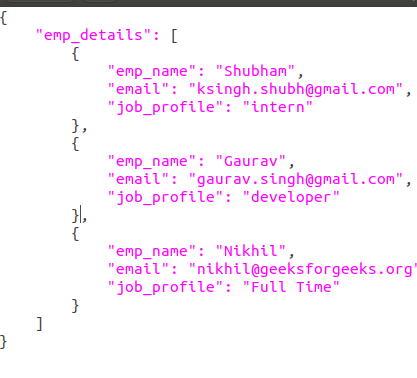
Here, we have used the open() function to read the JSON file. Then, the file is parsed using json.load() method which gives us a dictionary named data.
Python3
import json
# Opening JSON file
f = open('data.json',)
# returns JSON object as
# a dictionary
data = json.load(f)
# Iterating through the json
# list
for i in data['emp_details']:
print(i)
# Closing file
f.close()
Output:

Convert Python Dict to JSON
In the below code, we are converting a Python dictionary to a JSON object using json.dumps() method of JSON module in Python. We first import the JSON module and then make a small dictionary with some key-value pairs and then passed it into json.dumps() method with 'indent=4' to convert this Python dictionary into a JSON object. As we have given the value of indent to 4 there are four whitespaces before each data as seen in the output.
Python3
# Python program to convert
# Python to JSON
import json
# Data to be written
dictionary = {
"id": "04",
"name": "sunil",
"department": "HR"
}
# Serializing json
json_object = json.dumps(dictionary, indent = 4)
print(json_object)
Output{
"id": "04",
"name": "sunil",
"department": "HR"
}
The following types of Python objects can be converted into JSON strings:
Python objects and their equivalent conversion to JSON:
|
dict
| object
|
list, tuple
| array
|
str
| string
|
int, float
| number
|
True
| true
|
False
| false
|
None
| null
|
Writing JSON to a file in Python
We can write JSON to file using json.dump() function of JSON module and file handling in Python. In the below program, we have opened a file named sample.json in writing mode using 'w'. The file will be created if it does not exist. Json.dump() will transform the Python dictionary to a JSON string and it will be saved in the file sample.json.
Python3
# Python program to write JSON
# to a file
import json
# Data to be written
dictionary ={
"name" : "sathiyajith",
"rollno" : 56,
"cgpa" : 8.6,
"phonenumber" : "9976770500"
}
with open("sample.json", "w") as outfile:
json.dump(dictionary, outfile)
Output:

Python Pretty Print JSON
When we convert a string to JSON the data is in a less readable format. To make it more readable we can use pretty printing by passing additional arguments in json.dumps() function such as indent and sort_keys as used in the below code.
Python3
# Python program to convert JSON to Python
import json
# JSON string
employee ='{"id":"09", "name": "Nitin", "department":"Finance"}'
# Convert string to Python dict
employee_dict = json.loads(employee)
# Pretty Printing JSON string back
print(json.dumps(employee_dict, indent = 4, sort_keys= True))
Output{
"department": "Finance",
"id": "09",
"name": "Nitin"
}
Similar Reads
Read JSON file using Python The full form of JSON is JavaScript Object Notation. It means that a script (executable) file which is made of text in a programming language, is used to store and transfer the data. Python supports JSON through a built-in package called JSON. To use this feature, we import the JSON package in Pytho
4 min read
Read JSON file using Python The full form of JSON is JavaScript Object Notation. It means that a script (executable) file which is made of text in a programming language, is used to store and transfer the data. Python supports JSON through a built-in package called JSON. To use this feature, we import the JSON package in Pytho
4 min read
Reading and Writing JSON to a File in Python The full form of JSON is Javascript Object Notation. It means that a script (executable) file which is made of text in a programming language, is used to store and transfer the data. Python supports JSON through a built-in package called JSON. To use this feature, we import the JSON package in Pytho
3 min read
Reading and Writing JSON to a File in Python The full form of JSON is Javascript Object Notation. It means that a script (executable) file which is made of text in a programming language, is used to store and transfer the data. Python supports JSON through a built-in package called JSON. To use this feature, we import the JSON package in Pytho
3 min read
Append to JSON file using Python JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data format that stores data as key-value pairs within curly braces {}. Python's json module makes it easy to work with JSON data, whether you are parsing JSON strings, converting Python objects to JSON, or appending new data to existing JSON files.
2 min read
Append to JSON file using Python JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data format that stores data as key-value pairs within curly braces {}. Python's json module makes it easy to work with JSON data, whether you are parsing JSON strings, converting Python objects to JSON, or appending new data to existing JSON files.
2 min read