Priority CPU Scheduling with different arrival time - Set 2
Last Updated :
28 Dec, 2024
Prerequisite -Program for Priority Scheduling - Set 1
Priority scheduling is a non-preemptive algorithm and one of the most common scheduling algorithms in batch systems. Each process is assigned first arrival time (less arrival time process first) if two processes have same arrival time, then compare to priorities (highest process first). Also, if two processes have same priority then compare to process number (less process number first). This process is repeated while all process get executed.
Implementation -
- First input the processes with their arrival time, burst time and priority.
- First process will schedule, which have the lowest arrival time, if two or more processes will have lowest arrival time, then whoever has higher priority will schedule first.
- Now further processes will be schedule according to the arrival time and priority of the process. (Here we are assuming that lower the priority number having higher priority). If two process priority are same then sort according to process number.
Note: In the question, They will clearly mention, which number will have higher priority and which number will have lower priority. - Once all the processes have been arrived, we can schedule them based on their priority.
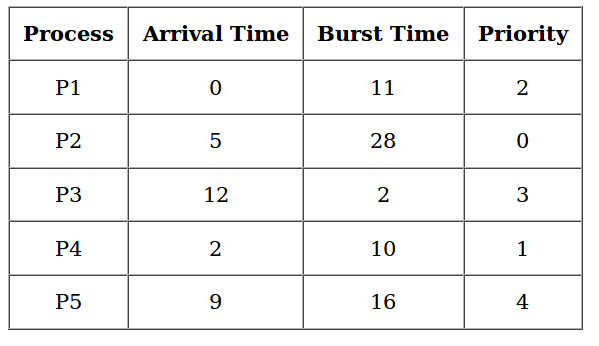
Gantt Chart -

Examples -
Input :
process no-> 1 2 3 4 5
arrival time-> 0 1 3 2 4
burst time-> 3 6 1 2 4
priority-> 3 4 9 7 8
Output :
Process_no arrival_time Burst_time Complete_time Turn_Around_Time Waiting_Time
1 0 3 3 3 0
2 1 6 9 8 2
3 3 1 16 13 12
4 2 2 11 9 7
5 4 4 15 11 7
Average Waiting Time is : 5.6
Average Turn Around time is : 8.8
C++
// C++ implementation for Priority Scheduling with
//Different Arrival Time priority scheduling
/*1. sort the processes according to arrival time
2. if arrival time is same the acc to priority
3. apply fcfs
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define totalprocess 5
// Making a struct to hold the given input
struct process
{
int at,bt,pr,pno;
};
process proc[50];
/*
Writing comparator function to sort according to priority if
arrival time is same
*/
bool comp(process a,process b)
{
if(a.at == b.at)
{
return a.pr<b.pr;
}
else
{
return a.at<b.at;
}
}
// Using FCFS Algorithm to find Waiting time
void get_wt_time(int wt[])
{
// declaring service array that stores cumulative burst time
int service[50];
// Initialising initial elements of the arrays
service[0] = proc[0].at;
wt[0]=0;
for(int i=1;i<totalprocess;i++)
{
service[i]=proc[i-1].bt+service[i-1];
wt[i]=service[i]-proc[i].at;
// If waiting time is negative, change it into zero
if(wt[i]<0)
{
wt[i]=0;
}
}
}
void get_tat_time(int tat[],int wt[])
{
// Filling turnaroundtime array
for(int i=0;i<totalprocess;i++)
{
tat[i]=proc[i].bt+wt[i];
}
}
void findgc()
{
//Declare waiting time and turnaround time array
int wt[50],tat[50];
double wavg=0,tavg=0;
// Function call to find waiting time array
get_wt_time(wt);
//Function call to find turnaround time
get_tat_time(tat,wt);
int stime[50],ctime[50];
stime[0] = proc[0].at;
ctime[0]=stime[0]+tat[0];
// calculating starting and ending time
for(int i=1;i<totalprocess;i++)
{
stime[i]=ctime[i-1];
ctime[i]=stime[i]+tat[i]-wt[i];
}
cout<<"Process_no\tStart_time\tComplete_time\tTurn_Around_Time\tWaiting_Time"<<endl;
// display the process details
for(int i=0;i<totalprocess;i++)
{
wavg += wt[i];
tavg += tat[i];
cout<<proc[i].pno<<"\t\t"<<
stime[i]<<"\t\t"<<ctime[i]<<"\t\t"<<
tat[i]<<"\t\t\t"<<wt[i]<<endl;
}
// display the average waiting time
//and average turn around time
cout<<"Average waiting time is : ";
cout<<wavg/(float)totalprocess<<endl;
cout<<"average turnaround time : ";
cout<<tavg/(float)totalprocess<<endl;
}
int main()
{
int arrivaltime[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int bursttime[] = { 3, 5, 1, 7, 4 };
int priority[] = { 3, 4, 1, 7, 8 };
for(int i=0;i<totalprocess;i++)
{
proc[i].at=arrivaltime[i];
proc[i].bt=bursttime[i];
proc[i].pr=priority[i];
proc[i].pno=i+1;
}
//Using inbuilt sort function
sort(proc,proc+totalprocess,comp);
//Calling function findgc for finding Gantt Chart
findgc();
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Anukul Chand.
import java.util.*;
class Process {
int at, bt, pr, pno;
Process(int pno, int at, int bt, int pr) {
this.pno = pno;
this.pr = pr;
this.at = at;
this.bt = bt;
}
}
public class PriorityScheduling {
static final int totalprocess = 5;
static Process proc[] = new Process[totalprocess];
static boolean comp(Process a, Process b) {
if (a.at == b.at) {
return a.pr < b.pr;
} else {
return a.at < b.at;
}
}
static void get_wt_time(int wt[]) {
int service[] = new int[totalprocess];
service[0] = proc[0].at;
wt[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < totalprocess; i++) {
service[i] = proc[i - 1].bt + service[i - 1];
wt[i] = service[i] - proc[i].at;
if (wt[i] < 0) {
wt[i] = 0;
}
}
}
static void get_tat_time(int tat[], int wt[]) {
for (int i = 0; i < totalprocess; i++) {
tat[i] = proc[i].bt + wt[i];
}
}
static void findgc() {
int wt[] = new int[totalprocess];
int tat[] = new int[totalprocess];
double wavg = 0, tavg = 0;
get_wt_time(wt);
get_tat_time(tat, wt);
int stime[] = new int[totalprocess];
int ctime[] = new int[totalprocess];
stime[0] = proc[0].at;
ctime[0] = stime[0] + tat[0];
for (int i = 1; i < totalprocess; i++) {
stime[i] = ctime[i - 1];
ctime[i] = stime[i] + tat[i] - wt[i];
}
System.out.println("Process_no\tStart_time\tComplete_time\tTurn_Around_Time\tWaiting_Time");
for (int i = 0; i < totalprocess; i++) {
wavg += wt[i];
tavg += tat[i];
System.out.println(proc[i].pno + "\t\t" + stime[i] + "\t\t" + ctime[i] + "\t\t" + tat[i] + "\t\t\t" + wt[i]);
}
System.out.println("Average waiting time is : " + wavg / totalprocess);
System.out.println("Average turnaround time : " + tavg / totalprocess);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arrivaltime[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int bursttime[] = {3, 5, 1, 7, 4};
int priority[] = {3, 4, 1, 7, 8};
for (int i = 0; i < totalprocess; i++) {
proc[i] = new Process(i + 1, arrivaltime[i], bursttime[i], priority[i]);
}
Arrays.sort(proc, (a, b) -> {
if (a.at == b.at) {
return a.pr - b.pr;
} else {
return a.at - b.at;
}
});
findgc();
}
}
# Python3 implementation for Priority Scheduling with
# Different Arrival Time priority scheduling
"""1. sort the processes according to arrival time
2. if arrival time is same the acc to priority
3. apply fcfs """
totalprocess = 5
proc = []
for i in range(5):
l = []
for j in range(4):
l.append(0)
proc.append(l)
# Using FCFS Algorithm to find Waiting time
def get_wt_time( wt):
# declaring service array that stores
# cumulative burst time
service = [0] * 5
# Initialising initial elements
# of the arrays
service[0] = 0
wt[0] = 0
for i in range(1, totalprocess):
service[i] = proc[i - 1][1] + service[i - 1]
wt[i] = service[i] - proc[i][0] + 1
# If waiting time is negative,
# change it o zero
if(wt[i] < 0) :
wt[i] = 0
def get_tat_time(tat, wt):
# Filling turnaroundtime array
for i in range(totalprocess):
tat[i] = proc[i][1] + wt[i]
def findgc():
# Declare waiting time and
# turnaround time array
wt = [0] * 5
tat = [0] * 5
wavg = 0
tavg = 0
# Function call to find waiting time array
get_wt_time(wt)
# Function call to find turnaround time
get_tat_time(tat, wt)
stime = [0] * 5
ctime = [0] * 5
stime[0] = 1
ctime[0] = stime[0] + tat[0]
# calculating starting and ending time
for i in range(1, totalprocess):
stime[i] = ctime[i - 1]
ctime[i] = stime[i] + tat[i] - wt[i]
print("Process_no\tStart_time\tComplete_time",
"\tTurn_Around_Time\tWaiting_Time")
# display the process details
for i in range(totalprocess):
wavg += wt[i]
tavg += tat[i]
print(proc[i][3], "\t\t", stime[i],
"\t\t", end = " ")
print(ctime[i], "\t\t", tat[i], "\t\t\t", wt[i])
# display the average waiting time
# and average turn around time
print("Average waiting time is : ", end = " ")
print(wavg / totalprocess)
print("average turnaround time : " , end = " ")
print(tavg / totalprocess)
# Driver code
if __name__ =="__main__":
arrivaltime = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
bursttime = [3, 5, 1, 7, 4]
priority = [3, 4, 1, 7, 8]
for i in range(totalprocess):
proc[i][0] = arrivaltime[i]
proc[i][1] = bursttime[i]
proc[i][2] = priority[i]
proc[i][3] = i + 1
# Using inbuilt sort function
proc = sorted (proc, key = lambda x:x[2])
proc = sorted (proc)
# Calling function findgc for
# finding Gantt Chart
findgc()
# This code is contributed by
# Shubham Singh(SHUBHAMSINGH10)
// C# implementation for Priority Scheduling with
// Different Arrival Time priority scheduling
// 1. sort the processes according to arrival time
// 2. if arrival time is same the acc to priority
// 3. apply fcfs
using System;
class Program
{
static int totalprocess = 5;
static int[][] proc = new int[totalprocess][];
static int[] arrivaltime = new int[] {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
static int[] bursttime = new int[] {3, 5, 1, 7, 4};
static int[] priority = new int[] {3, 4, 1, 7, 8};
// Driver code
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < totalprocess; i++)
{
proc[i] = new int[4];
proc[i][0] = arrivaltime[i];
proc[i][1] = bursttime[i];
proc[i][2] = priority[i];
proc[i][3] = i + 1;
}
Array.Sort(proc, (x, y) => x[2].CompareTo(y[2]));
Array.Sort(proc, (x, y) => x[0].CompareTo(y[0]));
Findgc();
}
// Using FCFS Algorithm to find Waiting time
static void GetWtTime(int[] wt)
{
// declaring service array that stores
// cumulative burst time
int[] service = new int[totalprocess];
// Initialising initial elements
// of the arrays
service[0] = 0;
wt[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < totalprocess; i++)
{
service[i] = proc[i - 1][1] + service[i - 1];
wt[i] = service[i] - proc[i][0] + 1;
// If waiting time is negative,
// change it o zero
if (wt[i] < 0)
{
wt[i] = 0;
}
}
}
// Filling turnaroundtime array
static void GetTatTime(int[] tat, int[] wt)
{
for (int i = 0; i < totalprocess; i++)
{
tat[i] = proc[i][1] + wt[i];
}
}
static void Findgc()
{
// Declare waiting time and
// turnaround time array
int[] wt = new int[totalprocess];
int[] tat = new int[totalprocess];
int wavg = 0;
int tavg = 0;
// Function call to find waiting time array
GetWtTime(wt);
// Function call to find turnaround time
GetTatTime(tat, wt);
int[] stime = new int[totalprocess];
int[] ctime = new int[totalprocess];
stime[0] = 1;
ctime[0] = stime[0] + tat[0];
Console.WriteLine("Process_no\tStart_time\tComplete_time\tTurn_Around_Time\tWaiting_Time");
// calculating starting and ending time
for (int i = 0; i < totalprocess; i++)
{
wavg += wt[i];
tavg += tat[i];
Console.WriteLine(proc[i][3] + "\t\t" + stime[i] + "\t\t" + ctime[i] + "\t\t" + tat[i] + "\t\t\t" + wt[i]);
// display the process details
if (i != totalprocess - 1)
{
stime[i + 1] = ctime[i];
ctime[i + 1] = stime[i + 1] + tat[i + 1] - wt[i + 1];
}
}
// display the average waiting time
// and average turn around time
Console.WriteLine("Average waiting time is: " + (double)wavg / totalprocess);
Console.WriteLine("Average turnaround time is: " + (double)tavg / totalprocess);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shiv1o43g
var totalprocess = 5;
var proc = [];
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
var l = [];
for (var j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
l.push(0);
}
proc.push(l);
}
function get_wt_time(wt) {
var service = new Array(5).fill(0);
service[0] = 0;
wt[0] = 0;
for (var i = 1; i < totalprocess; i++) {
service[i] = proc[i - 1][1] + service[i - 1];
wt[i] = service[i] - proc[i][0] + 1;
if (wt[i] < 0) {
wt[i] = 0;
}
}
}
function get_tat_time(tat, wt) {
for (var i = 0; i < totalprocess; i++) {
tat[i] = proc[i][1] + wt[i];
}
}
function findgc() {
var wt = new Array(5).fill(0);
var tat = new Array(5).fill(0);
var wavg = 0;
var tavg = 0;
get_wt_time(wt);
get_tat_time(tat, wt);
var stime = new Array(5).fill(0);
var ctime = new Array(5).fill(0);
stime[0] = 1;
ctime[0] = stime[0] + tat[0];
for (var i = 1; i < totalprocess; i++) {
stime[i] = ctime[i - 1];
ctime[i] = stime[i] + tat[i] - wt[i];
}
console.log("Process_no\tStart_time\tComplete_time\tTurn_Around_Time\tWaiting_Time"
);
for (var i = 0; i < totalprocess; i++) {
wavg += wt[i];
tavg += tat[i];
console.log(
proc[i][3] +
"\t\t" +
stime[i] +
"\t\t" +
ctime[i] +
"\t\t" +
tat[i] +
"\t\t\t" +
wt[i]
);
}
console.log("Average waiting time is : " + wavg / totalprocess);
console.log("average turnaround time : " + tavg / totalprocess);
}
var arrivaltime = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
var bursttime = [3, 5, 1, 7, 4];
var priority = [3, 4, 1, 7, 8];
for (var i = 0; i < totalprocess; i++) {
proc[i][0] = arrivaltime[i];
proc[i][1] = bursttime[i];
proc[i][2] = priority[i];
proc[i][3] = i + 1;
}
proc.sort(function (a, b) {
if (a[2] == b[2]) {
return a[0] - b[0];
} else {
return a[2] - b[2];
}
});
findgc();
// This code is contributed by shiv1o43g
Output:
Process_no Start_time Complete_time Turn_Around_Time Waiting_Time
1 1 4 3 0
2 5 10 8 3
3 4 5 2 1
4 10 17 13 6
5 17 21 16 12
Average Waiting Time is : 4.4
Average Turn Around time is : 8.4
Time Complexity: O(N * logN), where N is the total number of processes.
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Non-Preemptive Priority CPU Scheduling Algorithm
Similar Reads
Round Robin Scheduling Algorithm with Different Arrival Time Round Robin Scheduling is one of the most popular CPU scheduling algorithms used in operating systems. This algorithm is designed to handle processes efficiently by assigning a fixed time slice or quantum to each process. However, when processes arrive at different times, the scheduling becomes slig
15+ min read
Round Robin Scheduling Algorithm with Different Arrival Time Round Robin Scheduling is one of the most popular CPU scheduling algorithms used in operating systems. This algorithm is designed to handle processes efficiently by assigning a fixed time slice or quantum to each process. However, when processes arrive at different times, the scheduling becomes slig
15+ min read
Preemptive Priority CPU Scheduling Algorithm Preemptive Priority CPU Scheduling Algorithm is a pre-emptive method of CPU scheduling algorithm that works based on the priority of a process. In this algorithm, the scheduler schedules the tasks to work as per the priority, which means that a higher priority process should be executed first. In ca
15+ min read
Shortest Remaining Time First (Preemptive SJF) Scheduling Algorithm In this post, we will talk about the pre-emptive version of Shortest Job First (SJF) scheduling, called Shortest Remaining Time First (SRTF). In SRTF, the process with the least time left to finish is selected to run. The running process will continue until it finishes or a new process with a shorte
8 min read
Program for Preemptive Priority CPU Scheduling Implementing priority CPU scheduling. In this problem, we are using Min Heap as the data structure for implementing priority scheduling. In this problem smaller numbers denote higher priority. The following functions are used in the given code below: struct process { processID, burst time, response
15+ min read
Longest Remaining Time First (LRTF) CPU Scheduling Program We have given some processes with arrival time and Burst Time and we have to find the completion time (CT), Turn Around Time(TAT), Average Turn Around Time (Avg TAT), Waiting Time(WT), Average Waiting Time (AWT) for the given processes. Prerequisite: CPU Scheduling | Longest Remaining Time First (LR
15+ min read