Difference Between Paging and Segmentation
Last Updated :
12 Jul, 2025
Paging divides memory into fixed-size blocks called pages, which simplifies management by treating memory as a uniform structure. In contrast, segmentation divides memory into variable-sized segments based on logical units such as functions, arrays, or data structures.
Both methods offer distinct advantages and are chosen based on the specific needs and complexities of applications and system architectures. Often, modern systems combine both techniques to leverage the benefits of each.
Paging
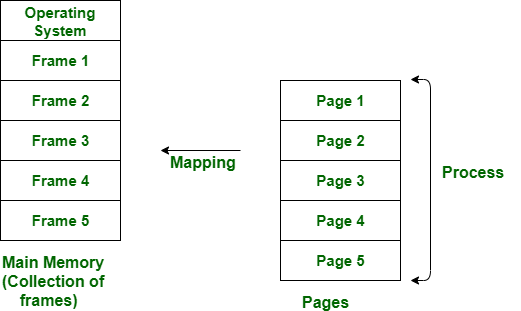
Paging is a method or technique which is used for non-contiguous memory allocation. It is a fixed-size partitioning theme (scheme). In paging, both main memory and secondary memory are divided into equal fixed-size partitions. The partitions of the secondary memory area unit and main memory area unit are known as pages and frames respectively.
Features of Paging
- Fixed-Size Division: Memory is divided into fixed-size pages, simplifying memory management.
- Hardware-Defined Page Size: Page size is set by hardware and is uniform across all pages.
- OS-Managed: The operating system handles paging, including maintaining page tables and free frame lists.
- Eliminates External Fragmentation: Paging avoids external fragmentation but can suffer from internal fragmentation.
- Invisible to User: Paging is transparent to programmers and users, simplifying software development.
Paging is a memory management method accustomed to fetching processes from the secondary memory into the main memory in the form of pages. in paging, each process is split into parts wherever the size of every part is the same as the page size.
The size of the last half could also be but the page size. The pages of the process area unit hold on within the frames of main memory relying upon their accessibility.
 Segmentation
Segmentation
Segmentation is another non-contiguous memory allocation scheme, similar to paging. However, unlike paging which divides a process into fixed-size pages segmentation divides memory into variable-sized segments that correspond to logical units such as functions, arrays, or data structures.
Features of Segmentation
- Variable-Size Division: Memory is divided into logical segments of varying sizes based on program structure.
- User/Programmer-Defined Sizes: Segment sizes are defined by the programmer or compiler, reflecting logical program units.
- Compiler-Managed: Segmentation is primarily managed by the compiler, with OS support for memory allocation.
- Supports Sharing and Protection: Segmentation facilitates sharing code/data between processes and easy implementation of protection.
- Visible to User: Segmentation is visible to programmers, allowing better control over logical memory organization.
In segmentation, both main memory and secondary memory are not divided into equal-sized partitions. Instead, they are split into segments of varying sizes. These segments are tracked using a data structure called the segment table.
The segment table stores information about each segment, primarily:
- Base: The starting physical address of the segment in memory.
- Limit: The length (or size) of the segment.
When accessing memory, the CPU generates a logical address composed of:
- A Segment Number
- A Segment Offset
The MMU (Memory Management Unit) uses the segment number to find the corresponding base and limit in the segment table. If the offset is less than the limit, the address is considered valid, and the physical address is computed by adding the offset to the base.
If the offset exceeds the limit, an error (segmentation fault) occurs, indicating an invalid address access attempt.
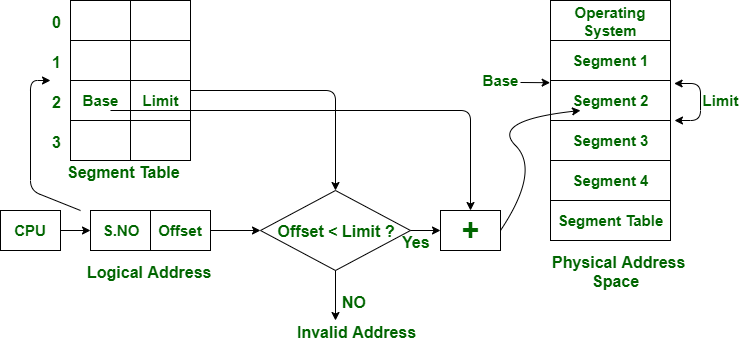
The above figure shows the translation of a logical address to a physical address.
Difference Between Paging and Segmentation
| Feature | Paging | Segmentation |
|---|
| Division Unit | Fixed-size pages | Variable-size segments |
|---|
| Managed By | Operating system | Compiler |
|---|
| Unit Size Determined By | Hardware | User/programmer |
|---|
| Address Structure | Page number + page offset | Segment number + segment offset |
|---|
| Data Structure Used | Page table | Segment table |
|---|
| Fragmentation Type | Internal fragmentation | External fragmentation |
|---|
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
|---|
| Programmer Visibility | Invisible to the user | Visible to the user |
|---|
| Sharing | Difficult | Easy |
|---|
| Data Structure Handling | Inefficient | Efficient |
|---|
| Protection | Hard to implement | Easier to apply |
|---|
| Size Constraints | Page = Frame size | No fixed size required |
|---|
| Memory Unit Perspective | Physical unit | Logical unit |
|---|
| System Efficiency | Less efficient | More efficient |
|---|
Similar Reads
Difference between Demand Paging and Segmentation Demand Paging is another segmentation technique which is used in operating system to manage system resources. It is therefore important for those who would understand various aspects of operating systems to have a clear distinction between them. This article shall provide a description of what each
5 min read
Difference Between Fragmentation and Segmentation in OS Memory management is an essential part of the operating system that concerns itself with the allocation, control, and release of memory resources. This is because every application that is executed will require some space for its data, code, and execution stacks, which also creates the need for appr
5 min read
Difference between Paging and Swapping in OS Proper memory management in any operating system is required for the smooth execution of numerous processes. Two fundamental techniques include paging and swapping. In Paging, the memory of a process is divided into fixed-size pages; this permits non-contiguous memory allocation and minimizes fragme
4 min read
Difference between Paging and Swapping in OS Proper memory management in any operating system is required for the smooth execution of numerous processes. Two fundamental techniques include paging and swapping. In Paging, the memory of a process is divided into fixed-size pages; this permits non-contiguous memory allocation and minimizes fragme
4 min read
Difference Between Fragmentation and Compaction In an operating system, memory management plays a vital role in maximum CPU utilization, when space is allocated to a process there is some loss of memory(fragmentation) leads to inefficient use of memory, and to reduce this loss one of the techniques (compaction) is used to optimize memory space.Wh
4 min read
Difference between Internal and External fragmentation Memory fragmentation is a prevalent problem in operating systems that can result in the inefficient use of memory resources. There are two types of fragmentation: internal and external, and they both have an impact on memory allocation and use. In this article, we are going to study the difference b
3 min read