|
| 1 | +# LeetCode 第 347 号问题:前 K 个高频元素 |
| 2 | + |
| 3 | +> 本文首发于公众号「五分钟学算法」,是[图解 LeetCode ](<https://github.com/MisterBooo/LeetCodeAnimation>)系列文章之一。 |
| 4 | +> |
| 5 | +> 个人网站:[https://www.cxyxiaowu.com](https://www.cxyxiaowu.com) |
| 6 | +
|
| 7 | +今天分享的题目来源于 LeetCode 上第 347 号问题:前 K 个高频元素。题目难度为 Medium,目前通过率为 56.9% 。 |
| 8 | + |
| 9 | +## 题目描述 |
| 10 | + |
| 11 | +给定一个非空的整数数组,**返回其中出现频率前 k 高**的元素。 |
| 12 | + |
| 13 | +**示例 1:** |
| 14 | + |
| 15 | +``` |
| 16 | +输入: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2 |
| 17 | +输出: [1,2] |
| 18 | +``` |
| 19 | + |
| 20 | +**示例 2:** |
| 21 | + |
| 22 | +``` |
| 23 | +输入: nums = [1], k = 1 |
| 24 | +输出: [1] |
| 25 | +``` |
| 26 | + |
| 27 | +**说明:** |
| 28 | + |
| 29 | +- 你可以假设给定的 k 总是合理的,且 1 ≤ k ≤ 数组中不相同的元素的个数。 |
| 30 | +- 你的算法的时间复杂度必须优于 O(n log n) , n 是数组的大小。 |
| 31 | + |
| 32 | +### 题目解析 |
| 33 | + |
| 34 | +### 解法一:粗暴排序法 |
| 35 | + |
| 36 | +最简单粗暴的思路就是 **使用排序算法对元素按照频率由高到低进行排序**,然后再取前 k 个元素。 |
| 37 | + |
| 38 | +以下十种排序算法,任你挑选! |
| 39 | + |
| 40 | +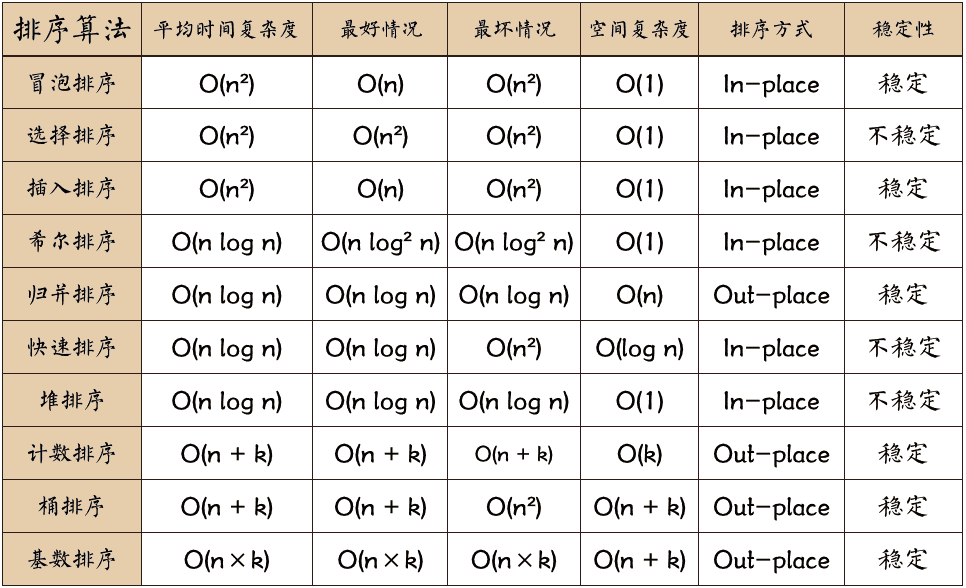 |
| 41 | + |
| 42 | +可以发现,使用常规的诸如 冒泡、选择、甚至快速排序都是不满足题目要求,它们的时间复杂度都是大于或者等于 O(n logn) ,而题目要求算法的时间复杂度必须优于 O(n log n) 。 |
| 43 | + |
| 44 | +#### 复杂度分析 |
| 45 | + |
| 46 | +- **时间复杂度**:O(nlogn),n 表示数组长度。首先,遍历一遍数组统计元素的频率,这一系列操作的时间复杂度是 O(n);接着,排序算法时间复杂度为O(nlogn) ;因此整体时间复杂度为 O(nlogn) 。 |
| 47 | +- **空间复杂度**:O(n),最极端的情况下(每个元素都不同),用于存储元素及其频率的 Map 需要存储 n 个键值对。 |
| 48 | + |
| 49 | +### 解法二:最小堆 |
| 50 | + |
| 51 | +题目最终需要返回的是前 k 个频率最大的元素,可以想到借助堆这种数据结构,对于 k 频率之后的元素不用再去处理,进一步优化时间复杂度。 |
| 52 | + |
| 53 | +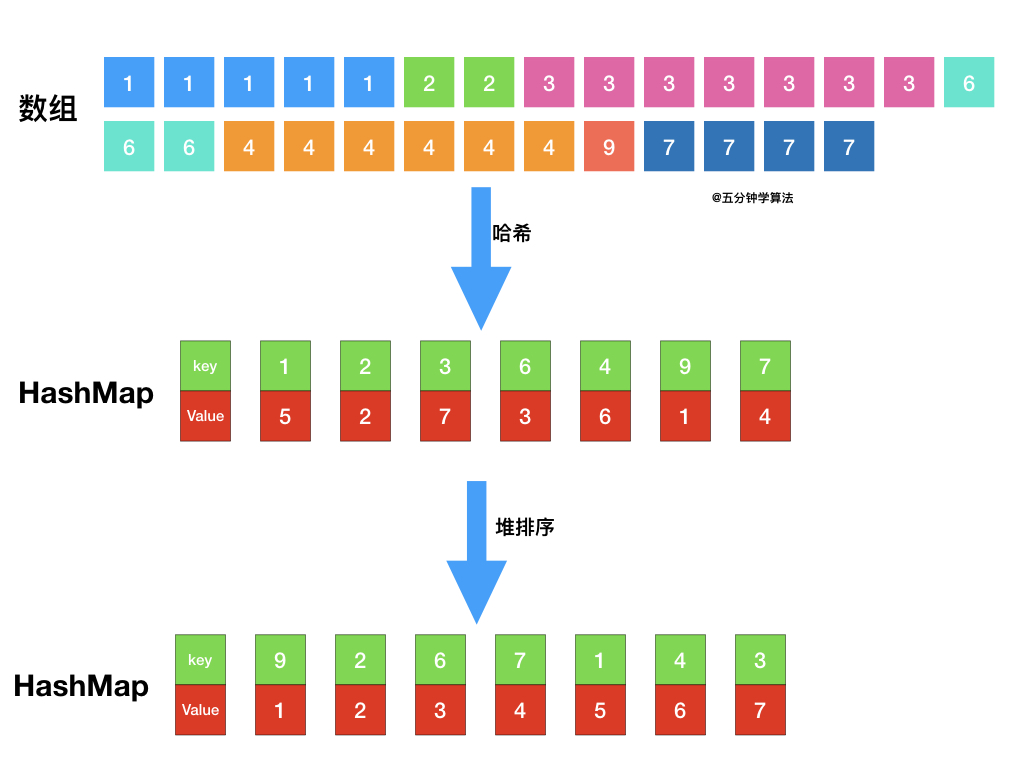 |
| 54 | + |
| 55 | +具体操作为: |
| 56 | + |
| 57 | +- 借助 **哈希表** 来建立数字和其出现次数的映射,遍历一遍数组统计元素的频率 |
| 58 | +- 维护一个元素数目为 k 的最小堆 |
| 59 | +- 每次都将新的元素与堆顶元素(堆中频率最小的元素)进行比较 |
| 60 | +- 如果新的元素的频率比堆顶端的元素大,则弹出堆顶端的元素,将新的元素添加进堆中 |
| 61 | +- 最终,堆中的 k 个元素即为前 k 个高频元素 |
| 62 | + |
| 63 | + |
| 64 | + |
| 65 | +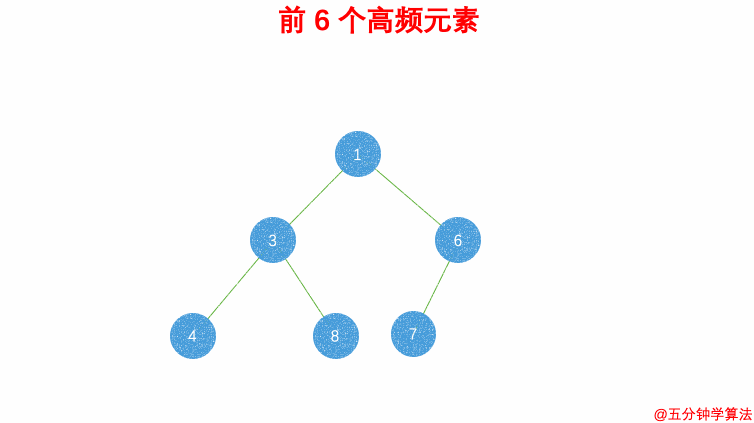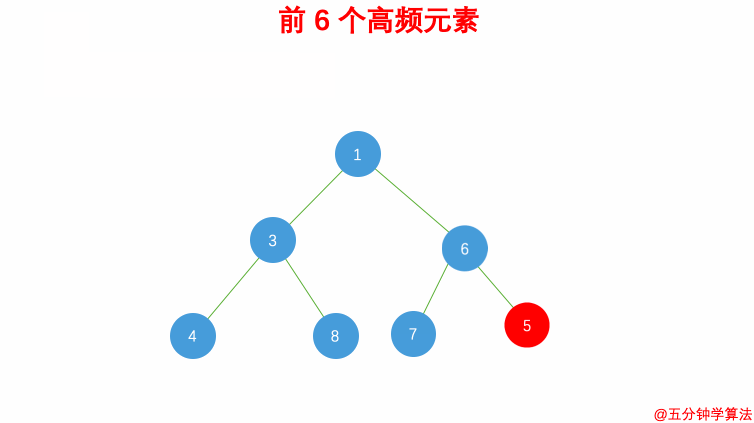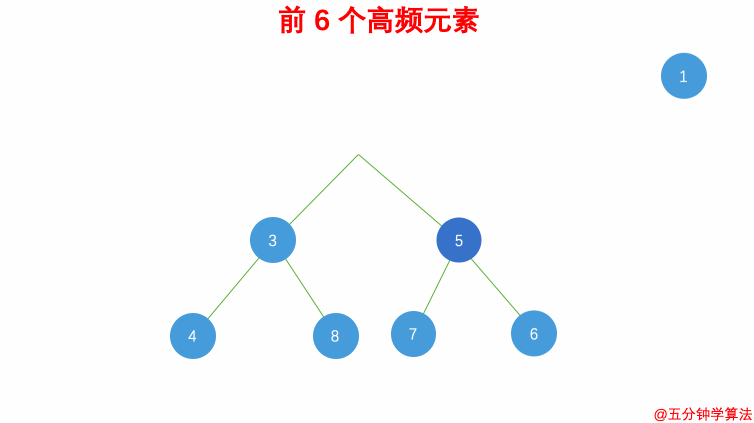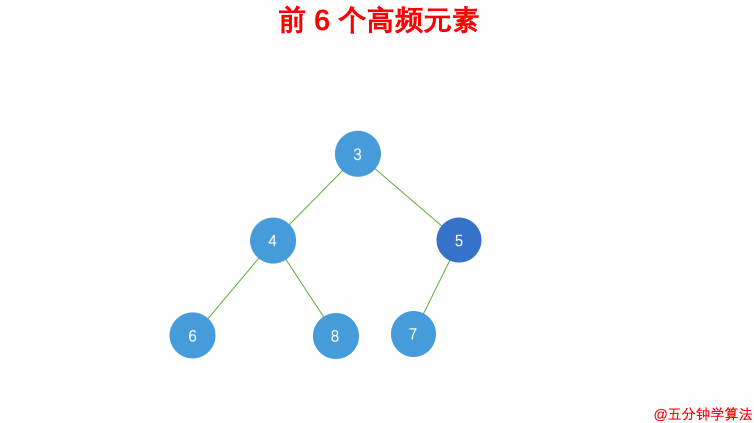 |
| 66 | + |
| 67 | +代码如下: |
| 68 | + |
| 69 | +```java |
| 70 | +class Solution { |
| 71 | + public List<Integer> topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) { |
| 72 | + // 使用字典,统计每个元素出现的次数,元素为键,元素出现的次数为值 |
| 73 | + HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap(); |
| 74 | + for(int num : nums){ |
| 75 | + if (map.containsKey(num)) { |
| 76 | + map.put(num, map.get(num) + 1); |
| 77 | + } else { |
| 78 | + map.put(num, 1); |
| 79 | + } |
| 80 | + } |
| 81 | + // 遍历map,用最小堆保存频率最大的k个元素 |
| 82 | + PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>() { |
| 83 | + @Override |
| 84 | + public int compare(Integer a, Integer b) { |
| 85 | + return map.get(a) - map.get(b); |
| 86 | + } |
| 87 | + }); |
| 88 | + for (Integer key : map.keySet()) { |
| 89 | + if (pq.size() < k) { |
| 90 | + pq.add(key); |
| 91 | + } else if (map.get(key) > map.get(pq.peek())) { |
| 92 | + pq.remove(); |
| 93 | + pq.add(key); |
| 94 | + } |
| 95 | + } |
| 96 | + // 取出最小堆中的元素 |
| 97 | + List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); |
| 98 | + while (!pq.isEmpty()) { |
| 99 | + res.add(pq.remove()); |
| 100 | + } |
| 101 | + return res; |
| 102 | + } |
| 103 | +} |
| 104 | + |
| 105 | +``` |
| 106 | + |
| 107 | +#### 复杂度分析 |
| 108 | + |
| 109 | +- **时间复杂度**:O(nlogk), n 表示数组的长度。首先,遍历一遍数组统计元素的频率,这一系列操作的时间复杂度是 O(n);接着,遍历用于存储元素频率的 map,如果元素的频率大于最小堆中顶部的元素,则将顶部的元素删除并将该元素加入堆中,**这里维护堆的数目是 k **,所以这一系列操作的时间复杂度是 O(nlogk)的;因此,总的时间复杂度是 O(nlogk) 。 |
| 110 | +- **空间复杂度**:O(n),最坏情况下(每个元素都不同),map 需要存储 n 个键值对,优先队列需要存储 k个元素,因此,空间复杂度是 O(n)。 |
| 111 | + |
| 112 | + |
| 113 | + |
| 114 | +### 解法三:桶排序法 |
| 115 | + |
| 116 | +首先依旧使用哈希表统计频率,统计完成后,创建一个数组,将频率作为数组下标,对于出现频率不同的数字集合,存入对应的数组下标即可。 |
| 117 | + |
| 118 | +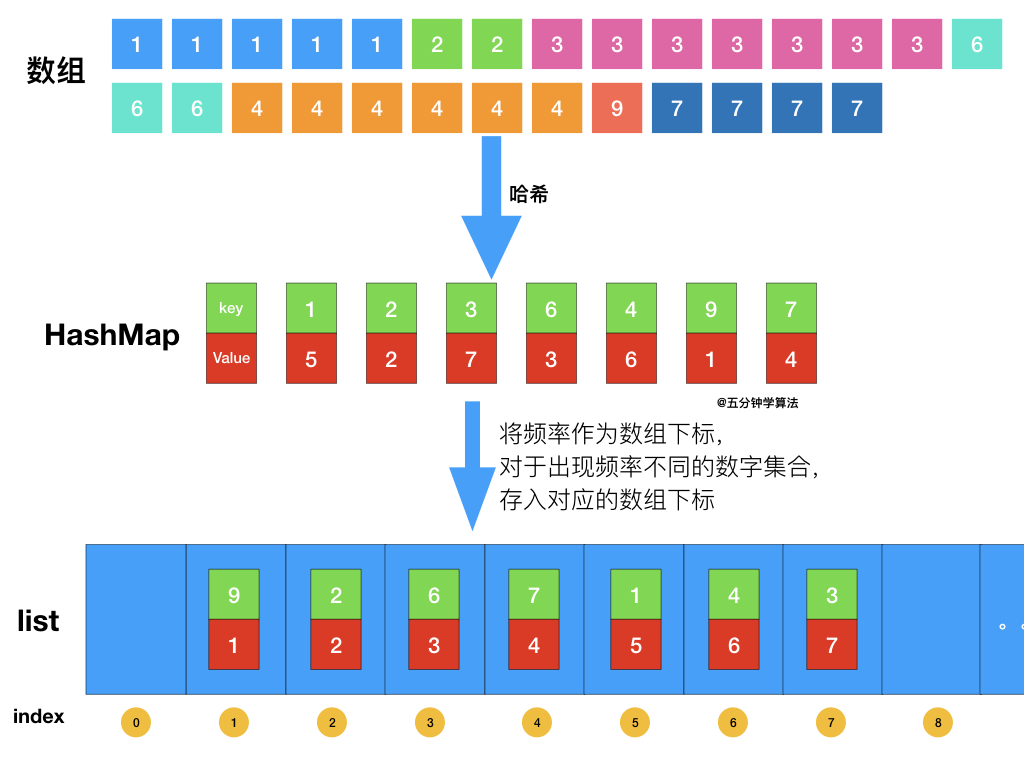 |
| 119 | + |
| 120 | +代码实现如下: |
| 121 | + |
| 122 | +```java |
| 123 | +//基于桶排序求解「前 K 个高频元素」 |
| 124 | +class Solution { |
| 125 | + public List<Integer> topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) { |
| 126 | + List<Integer> res = new ArrayList(); |
| 127 | + // 使用字典,统计每个元素出现的次数,元素为键,元素出现的次数为值 |
| 128 | + HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap(); |
| 129 | + for(int num : nums){ |
| 130 | + if (map.containsKey(num)) { |
| 131 | + map.put(num, map.get(num) + 1); |
| 132 | + } else { |
| 133 | + map.put(num, 1); |
| 134 | + } |
| 135 | + } |
| 136 | + |
| 137 | + //桶排序 |
| 138 | + //将频率作为数组下标,对于出现频率不同的数字集合,存入对应的数组下标 |
| 139 | + List<Integer>[] list = new List[nums.length+1]; |
| 140 | + for(int key : map.keySet()){ |
| 141 | + // 获取出现的次数作为下标 |
| 142 | + int i = map.get(key); |
| 143 | + if(list[i] == null){ |
| 144 | + list[i] = new ArrayList(); |
| 145 | + } |
| 146 | + list[i].add(key); |
| 147 | + } |
| 148 | + |
| 149 | + // 倒序遍历数组获取出现顺序从大到小的排列 |
| 150 | + for(int i = list.length - 1;i >= 0 && res.size() < k;i--){ |
| 151 | + if(list[i] == null) continue; |
| 152 | + res.addAll(list[i]); |
| 153 | + } |
| 154 | + return res; |
| 155 | + } |
| 156 | +} |
| 157 | +``` |
| 158 | + |
| 159 | +#### 复杂度分析 |
| 160 | + |
| 161 | +- **时间复杂度**:O(n), n 表示数组的长度。首先,遍历一遍数组统计元素的频率,这一系列操作的时间复杂度是 O(n);桶的数量为 n + 1,所以桶排序的时间复杂度为 O(n);因此,总的时间复杂度是 O(n)。 |
| 162 | +- **空间复杂度**:很明显为 O(n) |
| 163 | + |
| 164 | + |
| 165 | + |
0 commit comments